
For most people the thought of how do fungi get their food, really just never gets much consideration.
If you are an avid Gardner or beginner it is essential for your production to have at the bare minimums, some background on the whole process.
For this reason i created this post.
Fungi, just like many other living organisms need food in order to thrive.
However, fungi tend to be a little different from other plants. That is because fungi lack the capability to make their own food as they don’t have chlorophyll.
While most of the other plants photosynthesize in order to acquire food, fungi use different ways to get food from the environment.

Ascomycota
Credits: jacilluch [CC BY-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)]
To start with, fungi come in two categories as we have the beneficial fungi and the harmful fungi.
Both reproduce in diverse ways but at the end of the day, they all depend on other microorganisms to get food.
Fungi will in most cases will be evident in the dump and warm areas, as such conditions are the best for them.
In addition to that, fungi have spores which tend to be carried through either water or air to other organisms.
It could be other plants or animals where they get a great place to source their food.
During this time, the fungi kind of hibernates until they get a suitable and beneficial place they can transfer to.
But before anything else, let’s talk about how fungi reproduce.
How Do Fungi Reproduce?
Most of the species of fungi are holomorphs meaning that they have the capability of reproducing both asexually and sexually.
All this only depends on the current environmental conditions.
For the sexual reproduction, it helps the fungi to be able to form a wide variety of genetic lineages and variants.
Hence, the fungi are able to survive majorly through adaptation and genetic change even in unfriendly and unstable environments.
All in all, both of these reproduction systems are carried out in unique ways.

Shelf Fungi growing on a tree
Credits: Ronja Addams-Moring [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)]
In most eukaryotes, the basic reproduction concept involves the fusion of gametes that belong to different mating types in sexual reproduction.
This is followed by the meiosis process and thereafter there is the production of somewhat identical progeny that occurs in the asexual reproduction.
In other words, this is also known as mitosis.
All these reproductive processes that occur in fungi are aided by some specialized structures that are found in fungi that are known as spores.
However, you need to know that this is a little different from seeds and pollen in plants and sperm and egg in the animals.
In that case, let’s have a closer look at each of the reproduction methods as this will give you better insight.
Asexual Reproduction
Also known as the reproduction through the formation of spores. Sporulation, is a process through which haploid fungal cells are considered the parent produce other haloid spores.
These spores later mature and in the end become full independent haploid individuals.
These spores that are produced by the fungi are later on disseminated by either wind or water to diverse locations.
Where they tend to germinate under more favorable conditions.
At this point, the spores germinate to form hyphae which eventually mature to individual fungi.
The spores are as a result of the mitosis process in the parent cell. Hence they may differ in shape, size, as well as color depending on the species of fungus that was involved in the reproduction.
In addition to that, they can either be multi-cellular or unicellular.
There are also three diverse types of spores that are formed during this asexual reproduction based on their structure and type. This includes;
⦁ Sporangiospores; these are some kind of structure that forms on the hyphae with the aim of producing and storing spores.
The sporangium is further categorized into non-motile and motile spores. They are more common in the Rhizopus species.
⦁ Zoospores; these are similar to the sporangiospores although the structure that holds the sporangium, in this case, is known as the zoosporangium. The zoospores happen to be motile and they are most evident in the aquatic types of fungi.
⦁ Conidiospores; this refers to the spores that can either be multi-cellular, unicellular maybe motile and at the same time formed separately in different cells.
The conidiospores can be produced on the tip of the hyphae. Or still, it could be produced on the mycelium. Common examples of the same include; Penicillium and Aspergillus.
Sexual Reproduction
Reproduction cycle in fungi
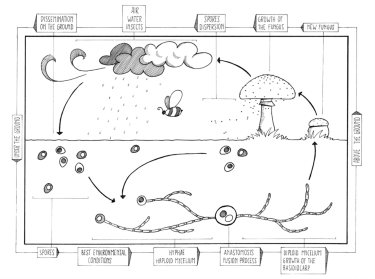
Credits: This image has been created during “DensityDesign Integrated Course Final Synthesis Studio” at Polytechnic University of Milan, organized by DensityDesign Research Lab in 2015. Image is released under CC-BY-SA licence. Attribution goes to “Anita Righetto, DensityDesign Research Lab”. [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)]
Unlike asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction in fungi features the fusion of two gametes.
That later on result in unique genetic variations in off springs that have been reproduced.
The genetic variation that occurs helps to equip these off springs with features as well as adaptations that foresee the survival and competition in their habitat.
More to that, with sexual reproduction, there is the production of two mating types during the reproduction process.
However, these mating types need to be well compatible with another and of the opposite sex too.
The mating type on the male side is known as the Antherida while the one on the female side is known as the Ascogonia.
The two mating types are referred to as the gametangia.
And depending on the position that the specific mating type takes, the sexual reproduction could either be defined as heterothallic or homothallic.
The heterothallic reproduction happens in cases where the mating types on both sides are present but in separate mycelia.
On the other hand, the homothallic reproduction occurs when the mating types from both sides are present but in the same mycelium.
In addition to that, this entire process of sexual reproduction occurs in three phases.
⦁ Plasmogamy; this happens to be the very first phase of the sexual reproduction. The mating types from opposite sides tend to fuse their cytoplasm although without any nuclear fusion. The cell that results from this fusion thereafter is known as the dikaryon. It consists of two nuclei from each of the mating types. However, this phase could be very long at times.
⦁ Karyogamy; this is a phase that is involved with the fusion of the nuclei that belongs to both of the involved matting types.
⦁ Meiosis; this is a process by which the cells are divided and eventually they form 4 daughter cells
Vegetative Reproduction
⦁ Fragmentation
In this reproduction process, the mycelium of the fungus tends to fragment to relatively smaller pieces. When that is done, each of the acquired pieces develops into a new and separate mycelium. This is a type of reproduction that is very common with moulds.
⦁ Fission
This is a common method of reproduction that majorly happens with unicellular fungi such as the unicellular yeast. In fission, the parent cell tends to elongate then cleaves itself in order to give you two daughter cells.
In fission, the cell division starts from the nucleus of the cell before it manages to extend all the way to the cytoplasm and finally the cell membrane. This process gives you two daughter cells in the end that thrive quite well independently.
⦁ Budding
This is a popular method of reproduction, especially in yeast. Budding begins with just a cell division that occurs in the parent fungus. Eventually, there is the formation of a bud or an outgrowth. This bud is attached to that parent structure until it fully matures.
After that, the bud falls off as a newly developed organism. In this case, the newly developed organism is completely identical to the parent cell.
Special Types of Vegetative Reproduction
Aside from the usual types of vegetative reproduction, there are a few special types that definitely occur under certain conditions. This includes; Rhizomorphs, chlamydospores, and Sclerotia.
⦁ Chlamydospores; these happen to be unicellular and elongated fragments that could either function in chains or as a single body. When the condition is unfavorable, these cells accumulated food and nutrients then build a thick wall. On the other hand, when the conditions are favorable they germinate into new cells that give us mycelia.
⦁ Rhizomorphs; they tend to be structures that resemble ropes and they are formed by hyphae that are entangled with each other. In unfavorable conditions, they remain dormant while the conditions are favorable they regrow into mycelia.
⦁ Sclerotia; they are similar to the Rhizomorphs in some way although they are covered by a thicker covering. These remain dormant and under favorable conditions, they germinate.
How do Fungi Obtain Nutrients to get their food?
I’m sure you are probably wondering how to fungi eat? Well, it’s pretty simple actually. More to that, it’s actually the same way that fungi obtain their nutrients. There are several ways through which fungi obtain nutrients which include:
⦁ Dead Organisms
One of the best examples of fungi in this section is mushrooms. Aside from the fact that you can make incredible delicacies from some species of mushrooms, they are also unique in their own way. To be more specific, mushrooms are saprophytic fungi. Meaning that they obtain their nutrients from dead organic materials.

Mushroom growing on dead plant material
Therefore, they are quite beneficial to the flora. That’s because saprophytic fungi are responsible for breaking down dead organic materials such as plants and animals.
Besides being useful in the natural environment, saprophytic fungi can also be used in the food production industry.
For instance, Penicillium camemberti grows on the surface of cheese such as Neufchâtel cheeses.
The growth of these fungi smooth ens the texture of the cheese hence making it sweeter than before.
⦁ Living Organisms
The other way that fungi are able to obtain nutrient is by eating living organisms in a relationship known as symbiosis. The symbiotic relationship can differ in several ways:
⦁ Parasitic relationship: Here, the fungi is only an absorber of beneficial nutrients from the host.
What’s more, the enzymes that the fungi use to break down the tissues can cause disease to the host organism.
A good example of saprophytic fungi is the Tinea corporis which is the fungus responsible for ringworm’s.
Once these fungi attach themselves on your skin, they grow their haustoria and penetrate your skin and tissue. They are able to penetrate your skin using their digestive enzymes.
⦁ Commensalism relationship: in this type of relationship, the fungi exist in a perfect relationship with the host. That’s because of the organism neither benefits nor harms the host.
⦁ Mutualism: in this particular case, both the host and the fungi benefit from the co-existence of the two. For instance, mycorrhiza exits in the roots of a plant. The mycorrhiza gets its glucose when the plant absorbs the glucose from the soil.
And there you have it. Fungi are able to obtain their nutrients from both dead and living organic materials. It all depends on the characteristics of the fungi plus its environment.
All in all, fungi are well adapted to their environment. That means that they can easily fit into most ecological systems without any difficulty.
Beneficial Fungi for Plants (Mycorrhiza)
Mycorrhiza fungi are one of the major soil components that make up the soil’s natural micro flora.
This means that mycorrhiza fungi are a very essential part of the ecosystem.
This fungus lives in a symbiotic relationship with most of the roots of vascular plants.
In this case, the mycorrhiza is used as root extensions. The hyphae of the fungi tend to travel even further that the roots of the plant can reach.
This way, the mycorrhiza allows the plant to enjoy more water and nutrients than what they could have reached without any help.
And since this happened to be a mutual benefit relationship, the fungi, on the other hand, get some small quantities of glucose and sugar.
And as we have seen, mycorrhiza plays a very vital role. In that, plants that form an association with mycorrhiza, they are likely to grow faster and more densely than other plants with no association.
On the same note, studies have shown that plants that have a relationship with mycorrhiza are definitely less likely to succumb to these soil-borne diseases.
Also, the mycorrhiza is capable of absorbing carbon dioxide from the environment. This means that mycorrhiza is a living sink for carbon.
In Summary…
As discussed in the article above, fungi could either be harmful or beneficial. This means that some types of fungi could have very many benefits in the ecosystem. For instance, mushrooms act as food and at the same time are able to break down dead organic materials. I hope that this post has helped in some way for you to get a better understanding of how do fungi get their food. Feel free to leave a comment and share!



